Analysis is the act of breaking something complex down into simpler parts that you examine in detail. To critically analyze a text or idea, identify its purpose, the question at issue, the author's point of view, the kinds of information involved, the reasoning, and the conclusions.
Unless a text is simply presenting information, it will often contain arguments. An argument is a series of statements that reach a logical conclusion that is intended to reveal the degree of truth of another statement. Arguments begin with premises (kinds of information) that are related to each other using valid forms of reasoning (a process) to arrive at a logical conclusion, new information. A logical conclusion is a new kind of information that is true in light of premises being true (if the premises are all facts) or seeming to be true (if the premises contain some opinions). A logical conclusion may be false, if the premises are false or the reasoning is poor.
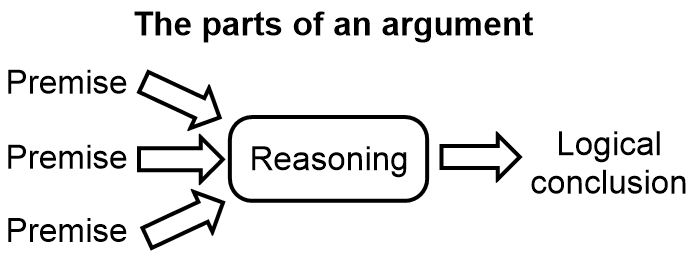
1. Identify the Purposes
All texts or ideas have a purpose.
- Take time to recognize the purpose of a text and always state your own purpose clearly when you write
- What do you think the author wants us to do, think about, or believe?
- Periodically check that the text or you are still on target with the purpose
2. Identify the Questions at Issue
When reasoning is present, the author is attempting to figure something out, to answer some question, or to solve a problem.
- Take time to clearly and precisely state the question at issue
- Express the question in several ways to clarify its meaning and scope
- Break down the question into sub questions
- Identify if the question has one right answer, is a matter of opinion, or requires reasoning from more than one point of view
3. Identify Points of View
All reasoning is done from some point of view. We often experience the world in such a way as to assume that we are observing things just as they are, as though we were seeing the world without the filter of a point of view. Nonetheless, we also recognize that others have points of view that lead them to conclusions we fundamentally disagree with. One of the key dispositions of critical thinking is the on-going sense that, as humans, we always think within a perspective, that we virtually never experience things totally and absolutely. There is a connection, therefore, between thinking so as to be aware of our assumptions and intellectual humility. Therefore, it is often helpful to open your mind and involve other people (friends, family, work colleagues) who help us see ourselves and our actions from unfamiliar perspectives. Sometimes reading books, watching videos, or having new experiences such as traveling to other cultures, going to college, or being an intern help us become aware of our assumptions. It is equally important to recognize that one person's is biased by their world view and experiences, and therefore all points of view should be examined critically.
- Identify your point of view
- Identify author's point of view
- Compare and contrast differing points of view
4. Distinguish Types of Information
Uncritical thinkers treat their conclusions as something given to them through experience, as something they directly observes in the world. As a result, they find it difficult to see why anyone might disagree with their conclusions. After all, they believe that the truth of their views is right there for everyone to see! Such people find it difficult to describe evidence without interpreting it through their point of view. Critical thinking requires the ability to label types of information and evaluate their quality before accepting an argument.
Information is true if it is accord accord with reality. Since our knowledge of reality is always incomplete, in practice truth is measured by its accord with the best information we have about reality. All information has an associated degree of belief (a feeling about truth) or confidence (the scientific term for statistical likelihood of truth) in its truth value. When analyzing, we are simply categorizing rather than evaluating the quality of the information.
All arguments are based on information. Premises are information that is used in the context of an argument. Information can be classified with four characteristics that describe the context in which it is used.
1. Evidence is information upon which conclusions are based. There are two categories of evidence:
- Facts (objective truth)
- Opinions (a feeling about the truth)
2. Assumptions are statements that we accept as true without proof or demonstration.
3. Conclusions are the results or reasoning, irrespective of their truth value.
4. Propaganda is information that is not objective and is used primarily to influence an audience and further an agenda
4A. Identify Evidence
Evidence is information that is relevant to question at issue. Both facts and opinions are evidence.
- Unless necessary facts unavailable, you should restrict your evidence to facts, verifiable information.
- Restrict your conclusions to those supported by the evidence you have.
Facts
A fact is an accurate description of an object, event, or statement that is independently verifiable by empirical means.
There are two distinct senses of the word "factual." The word may refer to a verified fact. However, "factual" may also refer to claims that are "factual in nature" in the sense that they can be verified or disproven by observation or empirical study, but those claims must be evaluated to determine if they are true. People often confuse these two senses, even to the point of accepting as true, statements which merely "seem factual", for example, "29.23 % of Americans suffer from depression." Before I accept this as true, I should assess it. I should ask such questions as "How do you know? How could this be known? Did you merely ask people if they were depressed and extrapolate those results? How exactly did you arrive at this figure?"
Purported facts should be assessed for their accuracy, completeness, and relevance to the issue. Sources of purported facts should be assessed for their qualifications, track records, and impartiality. Many students have experienced an education which stressed retention and repetition of factual claims. Such an emphasis stunts students' desire and ability to assess alleged facts, leaving them open to manipulation. Likewise, activities in which students "distinguish fact from opinion" often confuse these two senses. They encourage students to accept as true statements which merely "look like" facts.
To identify facts, look for these signal words in italics: "The annual report confirms ...," "Scientists have recently discovered ...," "According to the results of the tests...," "The investigation demonstrated ... "
Credible facts reference the observer of the information. You should accept a fact only after you have identified confirmation by many different independent observers and evaluated their credibility and potential bias. Even before this evaluation, you should reject a fact that does not have a clear source
As an example, in the debate we watched, Nick Gillespie says, "[drugs are] not addictive for 99 percent of people." This is factual only in the sense that may be empirically possible to measure, but you should not accept this as fact without more context such as a source.
If you have the opportunity, ask someone, "where did you get that information?" to give them the chance to confirm a fact. Until, you actually understand the limits and source of the fact, you should regard the information as suspicious and categorize it as an opinion that someone believes is true.
Opinions
An opinion is a statement that expresses either how a person feels about something or what a person thinks is true. With objective verification, opinions can become facts. If they cannot be proven or disproven, they will always be opinions.
Since we cannot examine the facts in all situations, sometimes we must rely on an opinion as evidence in an argument. Any conclusion derived from an argument that uses an opinion in place of a fact will generally be less reliable. You should always acknowledge such uncertainty when presenting such a conclusion.
- Look for these signal words in italics: "He claimed that...," "It is the officer's view that...," "The report argues that...," "Many scientists suspect that... "
- Some opinions are more reliable than others. An opinion that is based on the objective consideration of a large amount of incomplete information will be more reliable than an opinion based on one observation and a feeling.
- Understand that things are not always as they appear to be. At times, writers, whether consciously or not, will frame opinion as fact and vice versa.
- Note that statements can contain both fact and opinion. They should be separately when analyzing an argument.
4B. Identify Assumptions
An assumption is a statement that we accept as true without proof or demonstration. It is an unstated premise, presupposition, or opinion that is required to connect data to conclusions.
All human thought and experience is based on assumptions. Our thought must begin with something we believe to be true in a particular context. We are typically unaware of what we assume and therefore rarely question our assumptions. Much of what is wrong with human thought can be found in the uncritical or unexamined assumptions that underlie it. Identifying and evaluating accuracy and validity of assumptions is arguably the most important application of critical thinking. Accurate and valid assumptions can become facts.
Assumptions are often very difficult to identify. Usually they are something we previously learned and do not question. They are part of our system of beliefs. We assume our beliefs to be true and use them to interpret the world about us.
This packet of exercises has many excellent examples assumptions identified in short scenarios.
4C. Identify Conclusions
Conclusions are the results or reasoning.
In logic, conclusions can be categorized based on their truth value:
- Sound conclusions result from true premises and valid reasoning.
- Unsound conclusions result from false premises and/or invalid reasoning.
Additionally, conclusions are often categorized as either:
- accurate/inaccurate based on the truth of the premises
- logical/illogical based on the quality of the reasoning
- justified/unjustified based on whether or not the truth value has been critically evaluated
Conclusions also can be categorized based on their role in an argument:
- Inferences (conclusions from a single step of reasoning that are used as a premise in a successive argument)
- Drawn conclusions (conclusions that relate back to the question at issue)
It should be noted that different disciplines that study human thought (i.e. philosophy, cognitive psychology, artificial intelligence, etc.) define the distinction between a conclusion and an inference differently. To avoid confusion, I will make the following distinctions. When analyzing reasoning, a logical conclusion refers to the result of any argument. When analyzing a complex argument focused on a question at issue, an inference is a logical conclusion drawn from a single step in reasoning and may be used as information in the premise of a successive step of reasoning. A drawn conclusion describes a logical conclusion that specifically answers the question at issue by logically relating many inferences as premises. The example in this article, effectively illustrates my distinction between an inference and drawn conclusion(Note that other sources may define these word in the exact opposite way!).
Conclusions are generally straight-forward to identify in context. When analyzing a complex argument focused on a complex question at issue, inferences are often made implicitly in the course of reasoning. For this reason, an inference may be more difficult to identify. Critical thinkers try to monitor their inferences to keep them in line with what is actually implied by what they know. When speaking, critical thinkers try to use words that imply only what they can legitimately justify. They recognize that there are established word usages which generate established implications.
Examples:
- If we assume that it is dangerous to walk late at night in big cities and we move to Chicago, we will infer that it is dangerous to go for a walk late at night in Chicago. We probably take for granted our assumption that it is dangerous to walk late at night in big cities and in Chicago implicitly.
- To infer that an act that was murder, is to infer that it was intentional and unjustified. The implications of this inference are severe, thus sufficient evidence must exist to justify this opinion or fact.
A helpful tool is to first identify an inference (what do we infer from the situation being evaluated?) then identify an assumption that is the premise to that inference ("If the inference is true, what did I assume about the situation?"). Often an assumption you identify this way is an inference that can be further unpacked by repeating the second step to identify deeper core assumptions.
Situation: I heard a scratch at the door. I got up to let the cat in.
Inference: I inferred that the cat was at the door.
Ask: If that is true, what did I infer about the situation?
Assumptions: Only the cat makes that noise, and he makes it only when he wants to be let in.
Since different people can have difference assumptions, they will make different inferences about the reality of the same situation.
|
Person One |
Person Two |
|
Situation: A man is lying on the sidewalk. |
Situation: A man is lying on the sidewalk. |
|
Inference: That man is a bum. |
Inference: That man is in need of help. |
|
Ask: If that is true, what did I assume about him in this situation? |
Ask: If that is true, what did I assume about him in this situation? |
|
Assumption: Only bums lie on sidewalks. |
Assumption: Anyone lying on a sidewalk is in need of help. |
4D. Identify Propaganda
Propaganda is a special category of information that is not objective and is used primarily to influence an audience to reach a specific conclusion. Propaganda attempts to arouse emotions and biases to short-circuit rational judgment. The author of propaganda deliberately designs an argument that does not hold up to critical thinking. It's use indicates an intent to, at worst mislead, or at best persuade without the use of reasoning. Whether or not propaganda is ethical is a personal and context-dependent value judgment that is separate from critical thinking.
Students often find analysis of propaganda to be confusing because it is an extra feature of information, rather than its own type. Information that is propaganda can be any non-objective type (opinion, assumption, and/or inference) if it is deliberately used to manipulate opinions using poor reasoning. Moreover, propaganda quite utilizes poor reasoning—it often employs logical fallacies or takes advantage of cognitive biases to mislead.
The following is a list of common propaganda techniques:
- Bandwagon. It aims at persuading people to do a certain thing because many other people are doing it. An example can be a soft drink advertisement wherein a large group of people is shown drinking the same soft drink. People feel induced to opt for that drink as it is shown to be consumed by many. Similarly, by simply declaring without evidence that something is America's Favorite, significantly increases sales. Snob appeal is the reverse of bandwagon. It indicates that buying a certain product will make you stand out from the rest, as the masses won't afford to buy it.
- Card Stacking Propaganda. Now, this technique is perhaps most popularly used. It involves the deliberate omission of certain facts to fool the target audience. The term card stacking originates from gambling and occurs when players try to stack decks in their favor. A similar ideology is used by companies to make their products appear better than they actually are. Most brands use this propaganda technique to downplay unsavory details about their products and services. For instance, some companies may cleverly conceal "hidden charges" and only talk about the benefits of their products and services. Changing the shape of french fries so that one pays more for less food, still doesn't change the fact that eating fried food is unhealthy.
- Glittering Generalities Propaganda uses emotional appeal or/and vague statements to influence the audience. Advertising agencies thus use of phrases like as "inspiring you from within" or "to kick-start your day" to create positive anecdotes. This makes the product look more appealing, resulting in better sales.
- Hacking Identity: The Pride-Fear-Outrage-Hatred Formula. Critically examine when identity categories become significant to an argument. In some cases it may be appropriate, in others it may be an emotionally manipulative red herring.
- Example: In recent years, the Russian government has planted appeals to pride to amplify difference and strengthen online social communities. This is then followed by stories designed to invoke fear and outrage. A 2018 report to the United States Senate Select Committee on Intelligence details how these tactics are apparently designed to "hack" the minds of citizens in democratic nations into feeling disillusioned with social and political institutions. The goal is to weaken democratic participation and nudge countries towards increasingly pro-authoritarian values.
- Repetition. It is when the product name is repeated many times during an advertisement. This technique may use a jingle, which is appealing to the masses and fits in their minds. This takes advantage of the illusory truth effect, a cognitive bias that is encapsulated in the old adage, "if you tell a lie big enough and keep repeating it, people will eventually come to believe it." It is an unfortunate reality that the Internet is often used to make make untrue information seem true by repetition.
- Slogans. A slogan is a brief, striking phrase that may include labeling and stereotyping. Although slogans may be enlisted to support reasoned ideas, in practice they tend to act only as emotional appeals. Opponents of the US's invasion and occupation of Iraq use the slogan "blood for oil" to suggest that the invasion and its human losses was done to access Iraq's oil riches. On the other hand, supporters who argue that the US should continue to fight in Iraq use the slogan "cut and run" to suggest withdrawal is cowardly or weak. Similarly, the names of the military campaigns, such as "enduring freedom" or "just cause" can also be considered slogans, devised to influence people.
- Testimonial propaganda is popular advertising technique that uses renowned or celebrity figures to endorse products and services. Now in this case, when a famous person vouches for something, viewers are likely to take account of the credibility and popularity of that person. Watch Drake's Sprite commercial as an example.
Wikipedia has an extensive list of propaganda techniques with numerous examples.
5. Analyze Reasoning
The identification of poor reasoning invalidates the conclusion of an argument. The conclusion of the argument may or may not be true. You must formulate an alternative valid argue ment to support the conclusion.
5A. Identify Logical Fallacies
Fallacies are faulty reasoning used in the construction of an argument. This topic is so vast that I have created a separate fallacies of reasoning page.
5B. Identify Cognitive Biases
A cognitive bias is a cognitive shortcut that leads to a loss of objectivity. Cognitive biases can lead to irrational thought through distortions of perceived reality, inaccurate judgment, or illogical interpretation. By learning about some of the most common biases, you can learn and how to avoid falling victim to them.
The identification of cognitive biases at work in an argument should make you skeptical. Like fallacies, this topic is so vast that I have created a separate cognitive biases page to explain them.